Drought is a complex natural hazard that leads to significant water scarcity, impacting agriculture, food security, and various economic sectors. It is characterized by a prolonged deficiency in precipitation, affecting ecosystems over extended periods. Recent trends indicate an increase in the intensity and frequency of droughts, partly due to global warming. Various drought indices, including the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI), Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI), and Palmer Drought Severity Index (scPDSI), are utilized to assess drought conditions. Each index has unique advantages and limitations, leading researchers to often recommend using multiple indices for comprehensive evaluation.
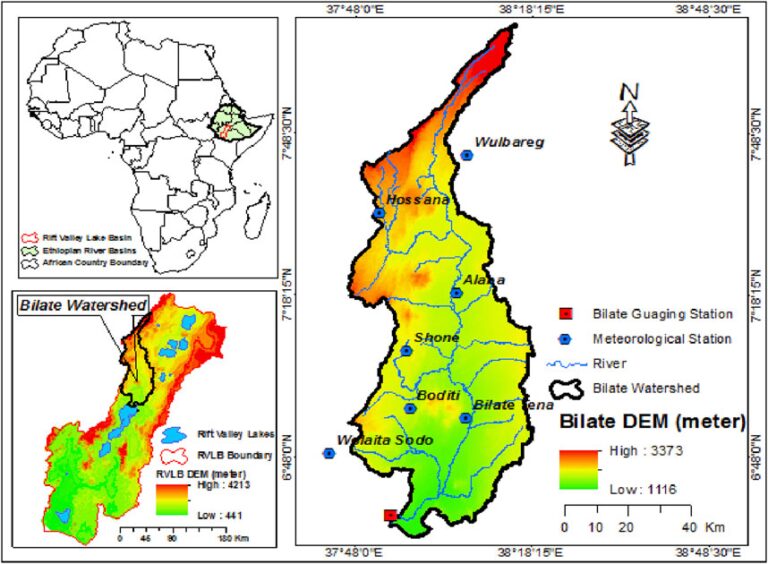
The study focuses on the Bilate River Watershed in Ethiopia, employing drought indices over four decades (1981-2019) to analyze drought characteristics using the Theory of Run and trend analysis. It revealed high correlations among indices at similar time scales, particularly effective for identifying historical drought events in notable years: 1984/85, 2000, 2002, and 2009. The analysis demonstrated that drought conditions have generally increased over time, with significant effects observed across different stations in the watershed. While Hossana and Wulbareg stations showed decreasing trends, the overall trajectory indicated worsening drought conditions, necessitating further research using enhanced data approaches, such as satellite imagery, for more accurate spatial assessments.