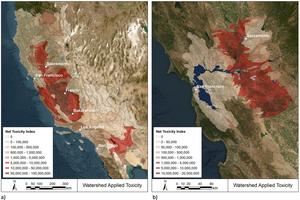
A study by Nicol Parker and Arturo A Keller from the University of California, Santa Barbara, published in PLOS Water, introduces the Environmental Release Tool (ERT), which evaluates the toxicity of pesticides in California’s agricultural watersheds. The ERT, based on US Geological Survey data, analyzes pesticide applications across 140 watersheds, revealing that a few pesticides and crops account for the majority of aquatic toxicity. By focusing on just two pesticides and sixteen sites, mitigation efforts could reduce around 90% of toxicity to aquatic life. The findings indicate that targeting a small number of high-toxicity watersheds could effectively lower overall pesticide environmental impact. However, the tool does not assess risks to human health or broader ecosystem effects. The study emphasizes the potential for selecting less toxic alternatives in agriculture to enhance toxicity reductions.
For access to the full article, visit: PLOS Water